Guided Reading & Analysis: Western Europe After the Fall of Rome

Guided Reading in THE Classroom: Strategies for Success
Few skills tin can benefit a child more throughout their life than the ability to read. It is a skill of such singular importance that information technology plays a role in most aspects of everyday classroom learning.
However, unfortunately for a skill of such importance, information technology isn't e'er possible to find the time for i:i reading with every educatee every day during the busy school schedule. Information technology is this trouble that guided reading is designed to accost.
What is Guided Reading?
Guided reading is a group method of pedagogy reading skills that can be used in identify of, though usually in add-on to, occasional 1:1 reading and discrete phonics education.
By and large speaking, guided reading involves teaching groups of children according to their ability levels. The exact number in each group will depend on the number of children in the class, every bit well as how well they do in a baseline reading assessment.
Normally, there are about v groups in the average class, though these groups may exist uneven in size and can be updated at various intervals throughout the year co-ordinate to private rates of progress as reflected in reading assessments.
In essence, guided reading is all about teaching to the various needs of the levelled groups in the classroom. It endeavours to instruct the students in a range of reading strategies that can be afterward applied independently to any new book the student encounters.
Agreement Reading Levels

Benchmark Assessment System 1, 2nd Edition By Fountas & Pinell Buy on Amazon
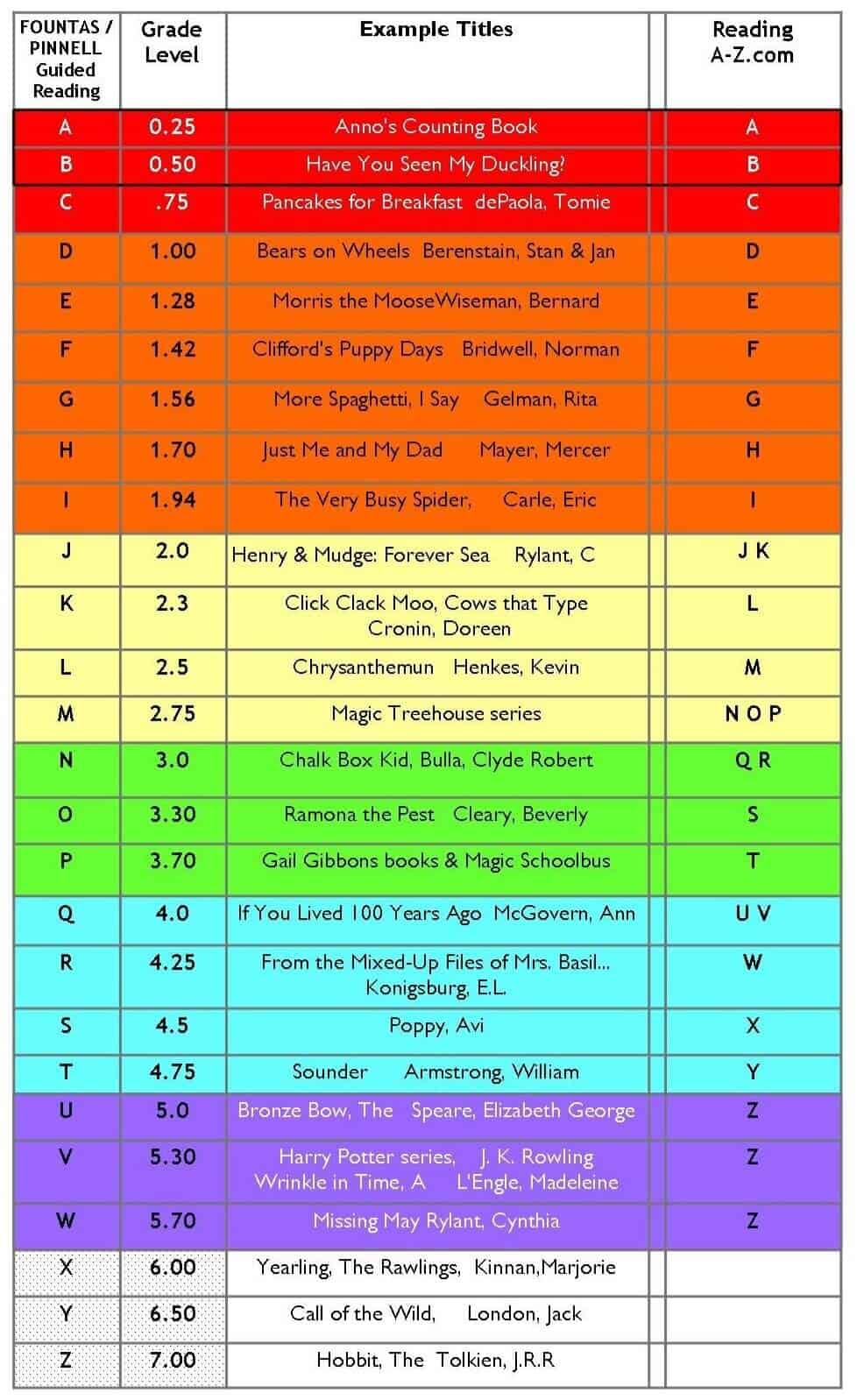
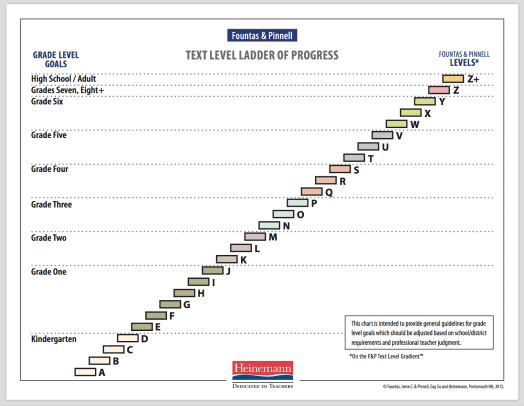
This tin can vary slightly depending on the region in which yous teach but the most commonly used method of guided reading assessment used is the alphabetical organization developed past Fountas, and Pinnell in the 1990s.
The levels range alphabetically from A to Z, with level A representing the lowest level and level Z the highest. This allows the teacher to work closely with each pupil to help them become improve readers past introducing increasingly challenging books while meeting the varying instructional needs of each child in the room.
It would be expected that equally a child progresses from kindergarten to the end of year 2 they would progress through all 26 levels.
Without an understanding of a students level, guided reading lacks whatever assessable growth.
Well-nigh every main and elementary schoolhouse volition take a copy of a criterion cess organisation similar to what you lot can see here, so track it downward and ensure you are familiar with it particularly if you piece of work in the junior levels.
GUIDED READING LEVEL Chart
READING ACTIVITIES FOR ANY TEXT

This massive collection of ☀️READING ACTIVITIES☀️ covers all essential reading skills for elementary/main students. NO PREP REQUIRED! works with all text and media types. Thousands of teachers take adopted this as a Go TO Resource for independent and group tasks.
- 60+ activities requiring students toWRITEin a range of genres and styles based on their text
- 40+ activities incorporating ARTISTIC and CREATIVE skills nigh their book.
- 30+ TECHNOLOGY based activities, including twenty open-concluded iPad and web based tasks
- 25+ GROUP based tasks
- 20+ tasks requiring Inquiry, Inquiry and EXPLORATION of concepts within a text.
- 50+ tasks you can employ with FILMS, GRAPHIC NOVELS and DIGITAL LITERACIES.
- fifteen+ activities involving DRAMA, MUSIC and ROLE PLAYING
- xv+ GRAPHIC ORGANIZERS that can be practical to whatever text
How is Guided Reading Organized?
To implement guided reading successfully, multiple copies of graded readers will exist needed. Y'all volition also need to assess each student's reading abilities to enable you lot to group them according to their specific power.
For our elementary-aged (or primary-aged) students, reading should be a daily activeness. Given the size of the average grade, guided reading is often the master method employed to teach reading.
If at that place are five guided reading power groups in the classroom, the teacher tin can expect to read with each grouping approximately every other day, for a minimum of twice per week. This is usually washed on a rota basis.
While the teacher reads with a group, the other groups tin can be engaged in other reading activities suitable for their level. These activities may include phonics work, sequencing activities, comprehension tasks, language games etc.
If at that place is a didactics assistant in the classroom, they can either support the children in completing these supplementary activities, or have the lead in a guided reading session besides.
The Guided Reading Area

Implementing guided reading successfully in the classroom requires considerable organisation. To make the most of the allotted time in the classroom it can be very helpful to dedicate a specific surface area to the exercise.
Some things you lot may wish to place in your guided reading surface area may include:
● Tables, chairs
● Posters/prompts of various reading strategies
● Listening area for audio versions of books
● Multiple copies of graded readers
● Book boxes
● Computers
● Mini whiteboards and markers
● Pencils, paper, Post-It notes etc
If classroom decoration is an surface area of interest to you be sure to cheque out this corking article which explores great means to enhance reading corners.
GUIDED READING ACTIVITIES & STRATEGIES
Every bit we have stated in the introduction, the main aim of guided reading is to instruct the students in the use of reading strategies that will eventually enable them to confidently and competently read whatever book by themselves.
We can grouping our strategies into three useful categories:
- Prediction – What do you recollect will happen next?
- Clarification & Questioning – Which parts of book did you find hard? What questions do you have about these?
- Summarizing – What is this book well-nigh? What happens?
ane. Prediction
Prediction encourages students to depict on their own prior learning and experiences to allow them to make educated guesses on what may follow in the story.
Prediction activities are great activities to hone your students' predictive abilities and comprehension skills, and they can exist repeated frequently. They also take the added advantage of requiring very petty preparation by the teacher.
Prior to get-go to read the called volume, some pre-reading work is necessary to focus the students' minds on the task at mitt.
Typically, this piece of work will brainstorm with an exam of the post-obit elements of the book:
● Title – What is the title of the volume? What does the title reveal about the volume?
● Blurb – What data does the blurb reveal? What expectations does it create?
● Author – Who is the author? What is the author'southward purpose in writing this book?
● Illustrator – Who is the illustrator? What clues do the illustrations give you lot about this text?
● Cover – What does the cover make y'all call up well-nigh? What expectations are created?
● Genre – What type of text is this? Is it fiction or nonfiction? How do yous know? What are our expectations of this genre in terms of subject and format?
While prediction begins with the mostly pre-reading activities outlined above, there will be aplenty opportunities for the student reader to make further predictions throughout the reading of the book likewise. For example, it is good practise to enquire the students, or encourage them to inquire themselves, prediction type questions at the end of a paragraph, section, or chapter.
Working on using prediction strategies in guided reading encourages the student to read closely for inferences and other clues that will signal the journey the text may take. Information technology also encourages the pupil to pay close attending to the content of the text as they read. This kind of holistic approach to reading improves overall comprehension of a text.
Prediction Graphic Organizer Activity
Provide the students with a T-Chart worksheet entitled 'My Predictions'. The chart should consist of 2 columns; one headed My Prediction and the other Why I Recall This. Provide a space to record the student's proper noun and the title of the text at the superlative of the canvas.
At whatever point during the reading of the text, you can instruct the students to stop and think about where this story is going. Students tin tape their predictions on their sheet, also every bit the reasons for thinking this.
This activity can serve well as a supplementary reading activity on days when the grouping is not scheduled to read with the class teacher.
2. Description and Questioning
In terms of guided reading, clarification refers to kickoff identifying the difficult parts of the text, before making sense of them through a variety of clarification techniques.
These techniques can be as elementary as looking up a word in a dictionary. There are other tools available to students, however. Ofttimes, when students look upwardly the meaning of a word in a dictionary it helps clarify the meaning of that role of the text in the brusk term, merely sometimes the give-and-take's definition is not retained for the adjacent time the educatee comes beyond it.
Sometimes it is amend for the pupil to use other techniques to piece of work out the meaning, such as employing contextual clues.
A COMPLETE DIGITAL READING UNIT FOR STUDENTS

Over 30 engaging activities for students to complete Before, DURING and After reading Any BOOK
- Compatible with all devices and digital platforms including GOOGLE CLASSROOM.
- Fun, Engaging, Open-Ended INDEPENDENT tasks.
Description and Question Prompts
Drills employing judgement starters are a nifty mode to effectively railroad train our students to clarify and question and to help internalise these strategies. Begin with the clarification prompts to help students identify the areas of the text they are unsure of, before moving to the question prompts to assistance them brainstorm to work out the meaning and significance inside the text.
Clarification Prompts:
● This part is difficult because…
● I didn't empathise when…
● I found it hard to work out the part where…
● I don't know what this means where it says…
When the students have identified the vocabulary, phrases, sentences, paragraphs, and sections that are giving them trouble, they can then move on to forming questions using the following question prompts:
Question Prompts:
● Who…
● What…
● Where…
● When…
● Why…
● How…
These prompts assistance students to place more closely the source of their defoliation when reading a text and to acquire to enquire for assistance. In the process of receiving an answer to their questions, they begin to broaden their understanding of a range of techniques they can later on employ in independent reading to clarify the meaning of a text for themselves.
In the context of guided reading, it can be helpful for students to piece of work together to form the questions to inquire their teacher.
Rather than directly answering the questions for the group, yet, teachers would practise well to encourage the students to work towards finding the answers for themselves, as this not only helps noesis retention simply improves their reading independence.
three. Summarizing READING
Summarizing is an important skill for students to develop. It helps students to identify the nearly important parts of a text or story and to learn to ignore irrelevant details and data too. Students who exercise summarizing learn to integrate the details and the master ideas of a text in a meaningful style. Summarization is useful for fiction and nonfiction genres alike.
A simple way to encourage your students to summarize a story is to enquire them to paraphrase information technology in their own words. As information technology volition be highly unlikely they will have memorized the entire story word for word, paraphrasing the story will allow you to assess their overall understanding of what they accept read.
Annotate and Summarize
To encourage your students to summarize a text, enquire them to respond the following four things:
● What are the primary ideas in the slice?
● What are the most important details or points made?
● What details or data is irrelevant or unnecessary?
● What are the keywords and phrases in the text?
If they have photocopies of the story, you may wish to accept them underline or highlight the information related to the above questions in dissimilar colors and then inquire them to retell the story in their own words after they have done this. Encourage them to use the keywords and phrases used in the text in their retelling also.
Become Guiding
Getting guided reading started in the classroom requires lots of planning and organisation at the beginning of the yr, but this initial investment of fourth dimension and attempt reaps rich rewards for students that is reflected in their rapid progress.
In one case clear procedures and routines are established, your students volition become more than adept at applying the broad range of strategies to a broad range of text types. This will go a long way to producing the confident and capable readers whatsoever teacher would be proud of. Now, get guiding!
VIDEO TUTORIALS on teaching guided reading
OTHER GREAT GUIDED READING ACTIVITIES
Content for this page has been written by Shane Mac Donnchaidh. A former principal of an international school and university English lecturer with 15 years of teaching and administration experience. Shane's latest Book the Complete Guide to Nonfiction Writing can be constitute here. Editing and support for this article have been provided by the literacyideas team.
Source: https://literacyideas.com/how-to-teach-guided-reading/





Post a Comment for "Guided Reading & Analysis: Western Europe After the Fall of Rome"